Critical Factors for Carrier-Grade LoRaWAN Gateways
Reducing annual expenditures by millions through the use of Carrier Grade Gateways
Carrier-grade requirements, first introduced in the late 1990s, ensure that telecom equipment meets mission-critical standards as they support people, businesses, and government operations. Initially focused on public wired and later wireless telecom, these standards have since been adopted for critical infrastructure such as VoIP and the Internet.
When designing and testing LoRaWAN gateways, several key areas must be addressed to ensure low operator costs and high network performance over a 5-10 year span. These areas include ruggedness and environmental protection, modular and scalable design, high receiver sensitivity and multi-channel support, simplified deployment and provisioning, multiple connectivity options, power resilience and alternatives, security features, local processing and low latency, compliance and certification, integration with network management platforms, support for future network architectures, and warranty and support services.
Ruggedness and Environmental Protection
A gateway's housing should be ruggedized to withstand harsh outdoor and industrial environments. This environmental protection includes dust, water jet resistance, and temperature extremes for long-term reliability.
Modular and Scalable Design
A modular hardware design allows for easy upgrades and maintenance, extending the gateway's lifecycle and enabling future-proof scalability to meet growing device densities and network demands.
High Receiver Sensitivity and Multi-Channel Support
To efficiently handle thousands of LoRaWAN devices, gateways must employ high receiver sensitivity and multi-channel capabilities, improving network capacity and reducing packet collisions.
Simplified Deployment and Provisioning
Features like auto-connect, auto-configure, and mobile provisioning platforms facilitate easier installation, reducing operational expenses in deployment and maintenance.
Multiple Connectivity Options
A gateway should support diverse backhaul connections, such as Ethernet, LTE cellular, and PoE, ensuring flexibility in different deployment scenarios and reliable real-time data transfer.
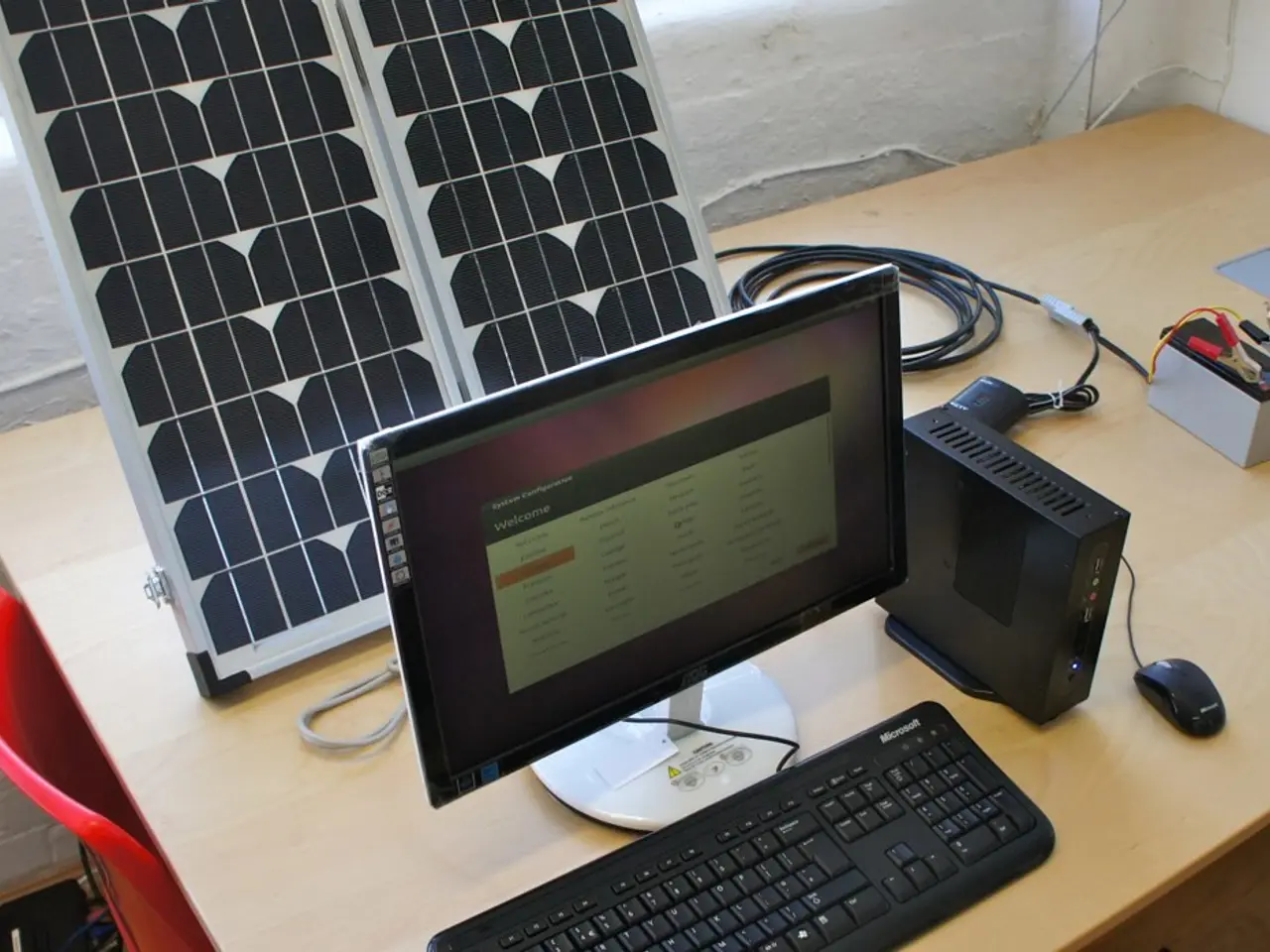
Power Resilience and Alternatives
Supporting multiple power sources, including solar, battery backup, and PoE, enhances operational continuity in remote or challenging environments, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Security Features
Security measures, such as Secure Boot, AES encryption, and secure communication protocols, protect device integrity, data confidentiality, and network trust throughout the gateway's lifetime.
Local Processing and Low Latency
Gateways should be capable of local sensing, control, and processing, enhancing reliability, reducing latency, and decreasing cloud service costs.
Compliance and Certification
Adherence to relevant industry standards and certifications, such as CE, FCC, and IEC safety standards, ensures gateway interoperability, regulatory acceptance, and long-term market viability.
Integration with Network Management Platforms
Compatibility with IoT management platforms facilitates smooth data integration, network monitoring, and remote management, aiding in optimizing overall network performance.
Support for Future Network Architectures
Designing gateways that can adapt to potential LoRaWAN network evolutions ensures they remain effective as technology and network topologies evolve.
Warranty and Support Services
Multi-year warranties and technical support reduce long-term operational risks and costs, ensuring sustained performance over the projected service period.
These factors collectively address the vital aspects of hardware durability, network capacity, ease of deployment, operational reliability, security, and future-proofing, ensuring low operator costs and high-performing carrier-grade LoRaWAN networks over extended periods.
- To achieve low operator costs and high network performance over a 5-10 year span, it is essential that carrier-grade LoRaWAN gateways also incorporate technology such as multi-channel support and security features like Secure Boot and AES encryption.
- As technology continues to evolve, carrier-grade LoRaWAN gateways must also be designed with technology that facilitates future network architectures, ensuring they remain effective as the network topologies and LoRaWAN network itself evolve.